Difference Between Horizontal and Vertical Machining Centers: Key Comparisons for Manufacturers
In the world of manufacturing, precision, efficiency, and adaptability are critical for success. When it comes to CNC machining, Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) and Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs) are two of the most widely used machines. Understanding the difference between horizontal and vertical machining center is crucial for making smart investment decisions. While both types are designed for milling, drilling, and cutting materials with high accuracy, their structural differences significantly influence their applications, performance, and cost-effectiveness. This article explores their key differences so manufacturers can choose the right equipment for their needs.
1. Orientation of the Spindle
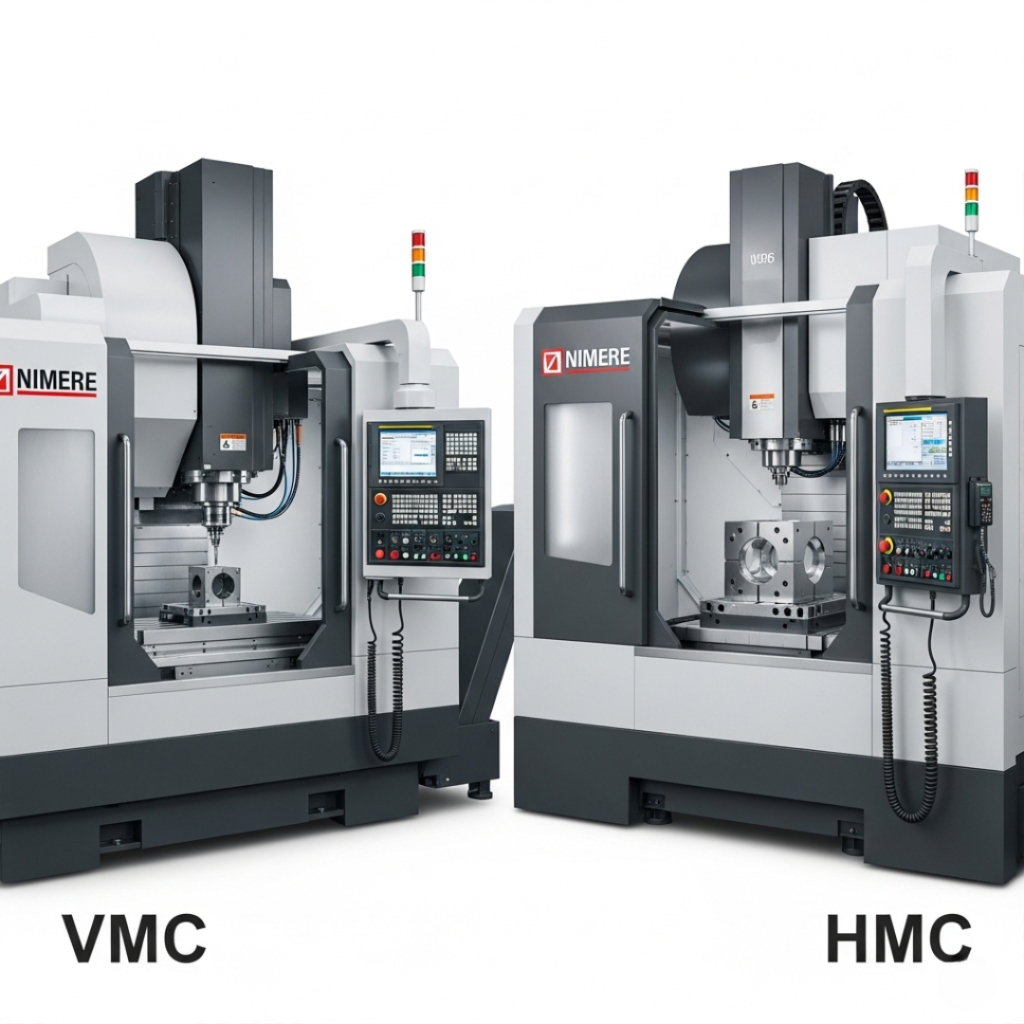

The most noticeable difference between these two machining centers is spindle orientation:
- Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs) have a vertically oriented spindle. The cutting tool approaches the workpiece from above, making them ideal for flat work such as plate work, mold cavities, and precision surface finishing.
- Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) feature a horizontally oriented spindle, with the cutting tool approaching from the side. This design allows for more efficient machining of multiple sides of a part without manual repositioning.
This variation in spindle direction affects everything from chip evacuation to production speed and tooling life.
2. Workpiece Setup and Accessibility
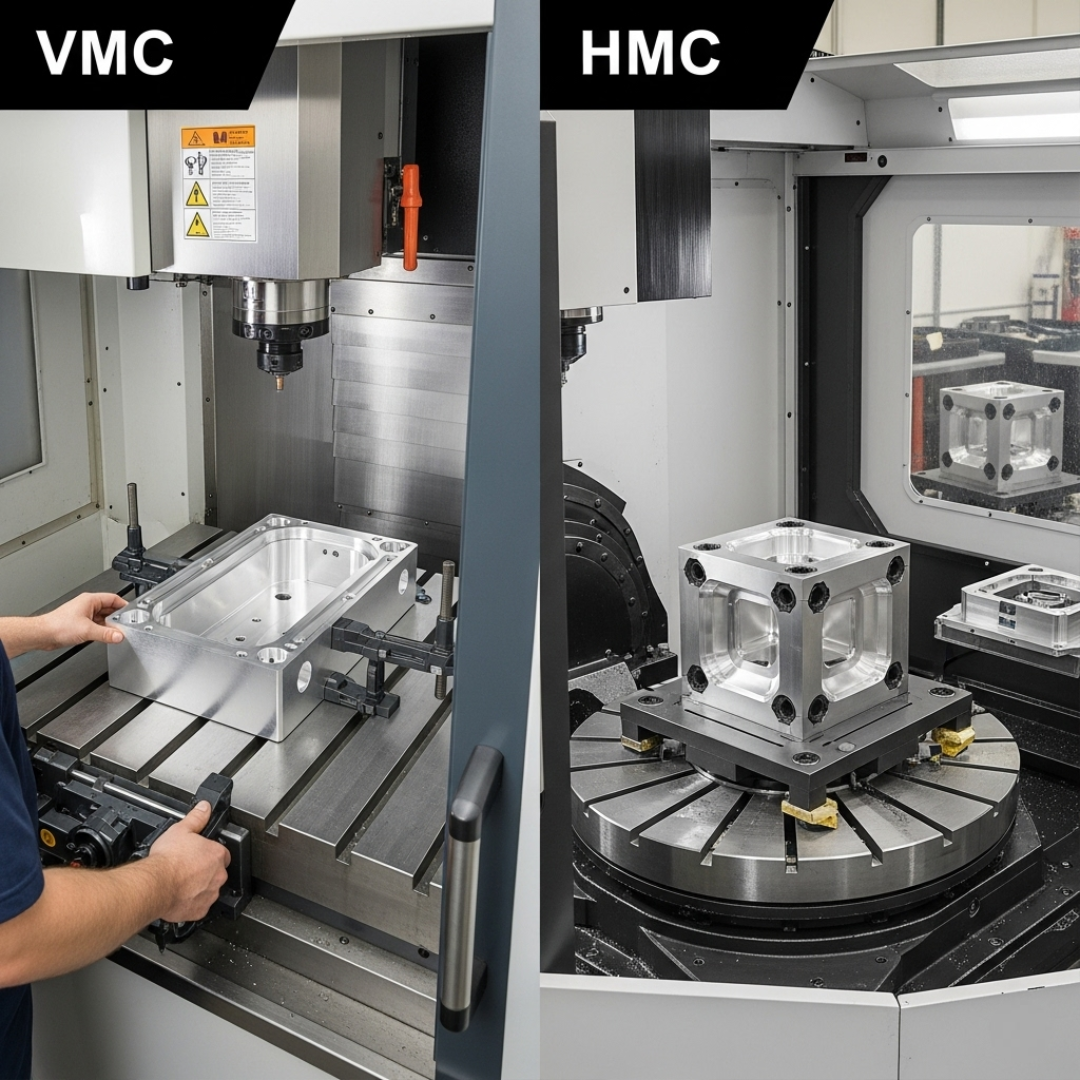
Workpiece handling is another area where these machines differ:
- VMCs are generally easier to set up and operate. Their open table design allows operators to quickly access the workpiece, making them ideal for small shops, custom fabrication, or jobs with frequent design changes.
- HMCs often use rotary tables or pallet systems, enabling multi-sided machining in a single setup. This minimizes downtime caused by part repositioning and increases output for high-volume runs.
For manufacturers focused on speed and consistency, HMCs have a clear advantage.
3. Chip Evacuation
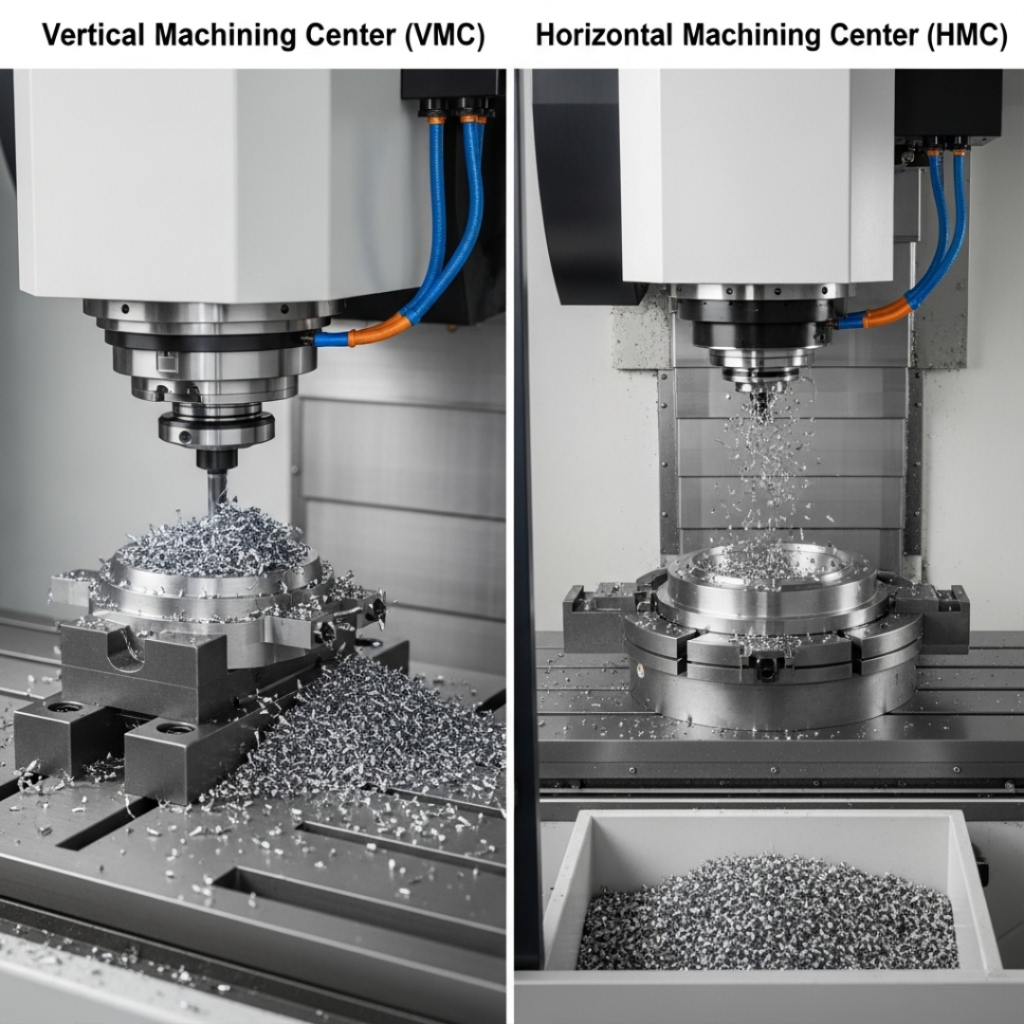

Chip management is critical for machining performance:
- VMCs can have chips accumulate on the table and workpiece, potentially affecting surface quality and requiring frequent cleaning.
- HMCs benefit from gravity-assisted chip removal. Chips naturally fall away from the work area, leading to cleaner cuts, reduced tool wear, and longer tool life.
For projects involving heavy material removal, the chip clearance advantage of HMCs can improve both quality and efficiency.
4. Production Speed and Automation
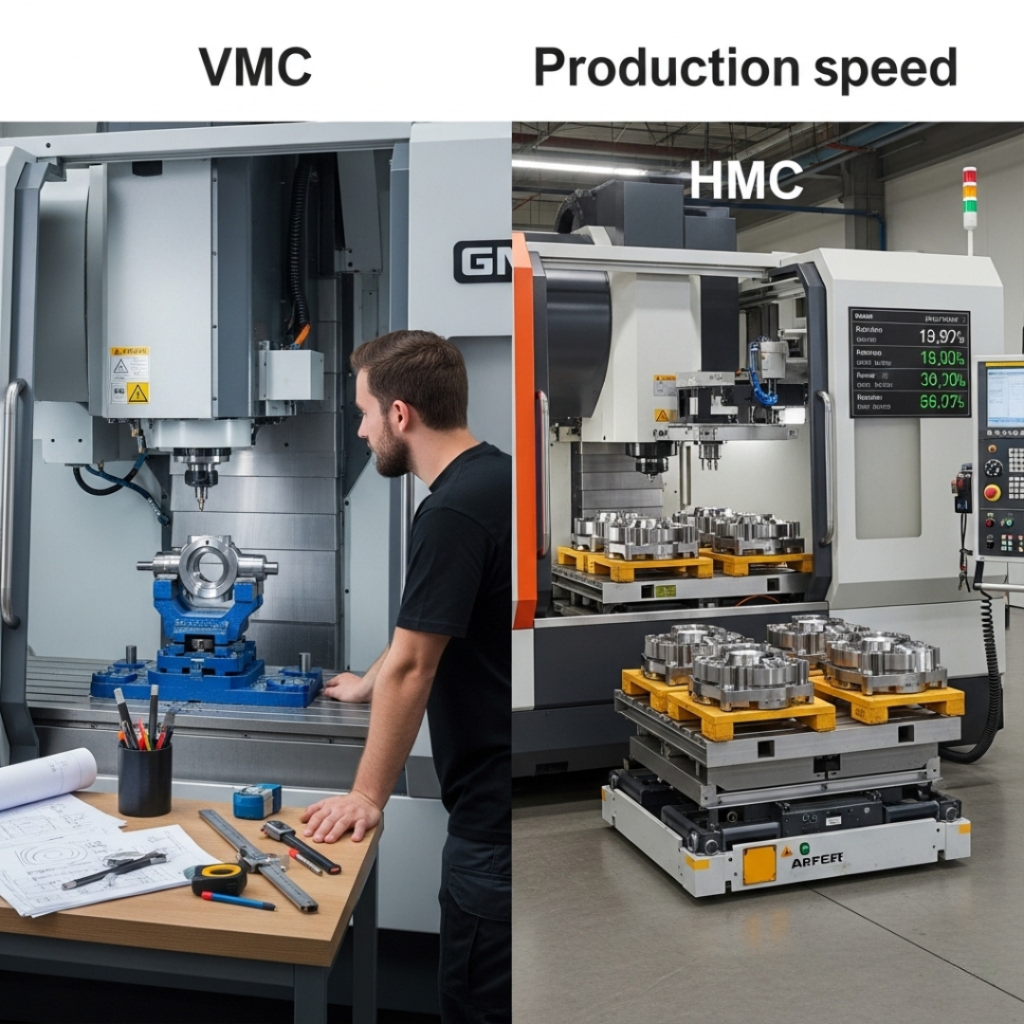
Production requirements often determine machine choice:
- VMCs are cost-effective for low- to medium-volume jobs, prototypes, and short runs. They can be automated but typically require more frequent operator intervention.
- HMCs are built for continuous, unattended operation. With multi-pallet changers, they can run for long periods without manual input, making them ideal for large-scale manufacturing.
The difference here boils down to whether your business needs flexibility or high throughput.
5. Cost Considerations

Budget is always a factor in equipment decisions:
- VMCs typically have a lower initial purchase price, making them accessible for startups and small-scale operations.
- HMCs require higher upfront investment but can deliver long-term cost savings in mass production through faster cycle times and reduced labor.
While the initial price may sway smaller shops toward VMCs, the return on investment from HMCs can be substantial in high-demand environments.
6. Applications
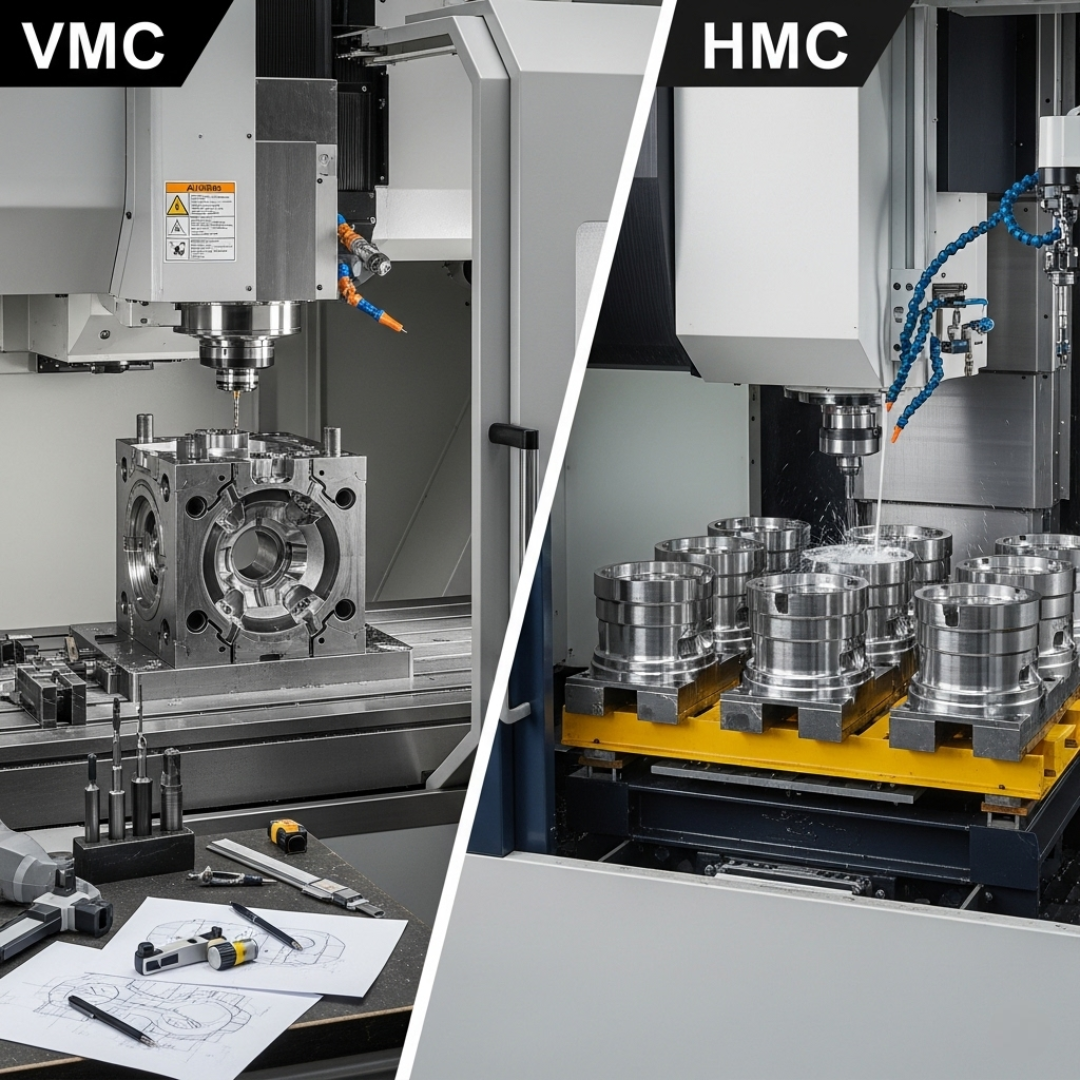

Different machining centers excel in different roles:
- VMCs are best for mold making, die sinking, prototyping, and custom one-off parts.
- HMCs are ideal for high-volume production, large and heavy parts, multi-face machining, and components requiring tight tolerances across multiple planes.
By matching the right machine to the right job, manufacturers can maximize productivity and quality.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between horizontal and vertical machining center helps manufacturers choose machines that match their specific production needs. VMCs offer simplicity, affordability, and ease of use, making them perfect for smaller runs and custom work. HMCs, with their superior chip evacuation, multi-sided machining capabilities, and automation readiness, excel in mass production environments.
If you’re ready to invest in the right machining solution, Can Star Industrial can guide you in selecting the perfect equipment to boost productivity, improve precision, and keep your business competitive in today’s manufacturing industry.
